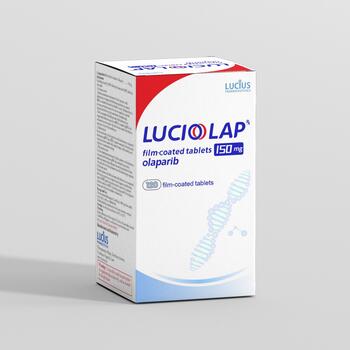
奥拉帕利 (Olaparib) 150mg
1. Composition:
The active ingredient of Olaparib is Olaparib, with the chemical name 4-[(3-{[4-(Cyclopropylcarbonyl)piperazin-1-yl]carbonyl}-4-fluorobenzyl)carbamoyl]phthalazin-1(2H)-one**. Its molecular formula is C24H23FN4O3, and its molecular weight is 434.47 g/mol.
2. Pharmacodynamics:
Olaparib inhibits the activity of PARP (poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase), preventing cancer cells from repairing their DNA damage, particularly in those cells that rely on BRCA gene function. Cancer cells with BRCA mutations have lost a key pathway for repairing DNA damage (the homologous recombination repair pathway). By inhibiting PARP, Olaparib causes these cancer cells to accumulate lethal DNA damage, ultimately leading to their death.
The main therapeutic effects include:
- Significant efficacy against ovarian cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer with BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations.
- Prolonging progression-free survival (PFS), especially in patients with residual cancer after chemotherapy.
- May be used in first-line or second-line treatment, depending on the patient's genetic mutation status and disease progression.
3. Usage:
Olaparib is usually administered in the form of oral capsules or tablets. The 50 mg dose of Olaparib is available in capsule form, with a recommended dosage typically being 300 mg (6 capsules of 50 mg) twice daily, although the exact dosage may be adjusted based on the patient’s physical condition, disease progression, and side effects.
- It can be taken with or without food.
- Patients should follow their doctor's instructions when taking the medication and should not change the dosage or stop taking the drug without medical advice.
4. Research & Development History
Olaparib is the first approved PARP inhibitor developed by **AstraZeneca**. The development of this drug began in the early 2000s, primarily targeting cancer patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, as these mutations make patients sensitive to DNA repair inhibitors. Olaparib has shown significant efficacy in clinical trials for patients with advanced or recurrent ovarian cancer. In 2014, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first approved Olaparib for the treatment of ovarian cancer with BRCA mutations. Subsequently, Olaparib has gradually been extended to other cancer types, such as breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer.
5. Mechanism of Action:
The core mechanism of Olaparib is to inhibit the activity of PARP enzymes, thereby preventing DNA repair. Under normal circumstances, PARP enzymes help repair single-strand DNA breaks. If this repair is inhibited, the DNA breaks accumulate and convert into double-strand breaks, which normal cells can repair through homologous recombination. However, for cancer cells with BRCA gene mutations, the homologous recombination repair function is impaired, making it impossible to repair these double-strand breaks, ultimately leading to cancer cell death.
This "synthetic lethality" mechanism makes Olaparib highly selective for BRCA-mutated cancers while reducing damage to normal cells, thereby minimizing the common systemic side effects of chemotherapy drugs.
6. Summary:
Olaparib is an effective anti-cancer drug for patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations. By inhibiting PARP enzymes, it interferes with the DNA repair mechanisms of cancer cells, resulting in cancer cell death, particularly in ovarian cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and prostate cancer caused by BRCA mutations. As part of targeted therapy, Olaparib significantly extends the progression-free survival and overall survival of these patients.